Stream Replication
You can replicate streams to other Data Fabric clusters worldwide, or to other streams within a Data Fabric cluster.
There are many scenarios in which replicating HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric Streams streams can be useful.
Basic Primary-Secondary Replication
For example, suppose that your company has a factory in Nagoya, and
sensors in the equipment track different metrics. The sensors are producers publishing
messages to a stream named metrics. The applications that use the collected
metrics would read the messages from the stream, playing the role of consumers. With
replication, the factory could create a stream in the nagoya cluster and
maintain a backup of the stream in the nagoya_ha cluster.
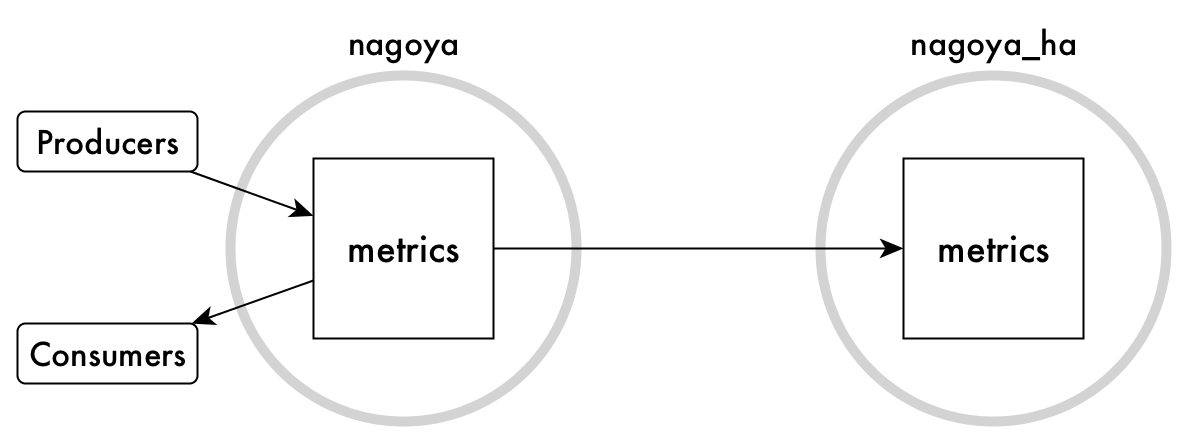
This type of replication is called basic primary-secondary replication because
replication is in one direction only. The metrics stream in the nagoya_ha
cluster is considered to be a replica. The original metrics stream is
considered to be the upstream source for the replica. This type of replication
is simple to set up with the command maprcli stream replica
autosetup.
metrics streams to a
backup. 
Many-to-One Replication
Your company's
headquarters are in San Francisco and you want data analysts there to analyze all data
company-wide. You can replicate the two metrics streams that are in the
your factories to the metrics stream in the sanfrancisco
cluster. In this scenario, the replica is the metrics stream in the
sanfrancisco cluster. This replica has two upstream sources: the
metrics streams that are replicated from the two factories.
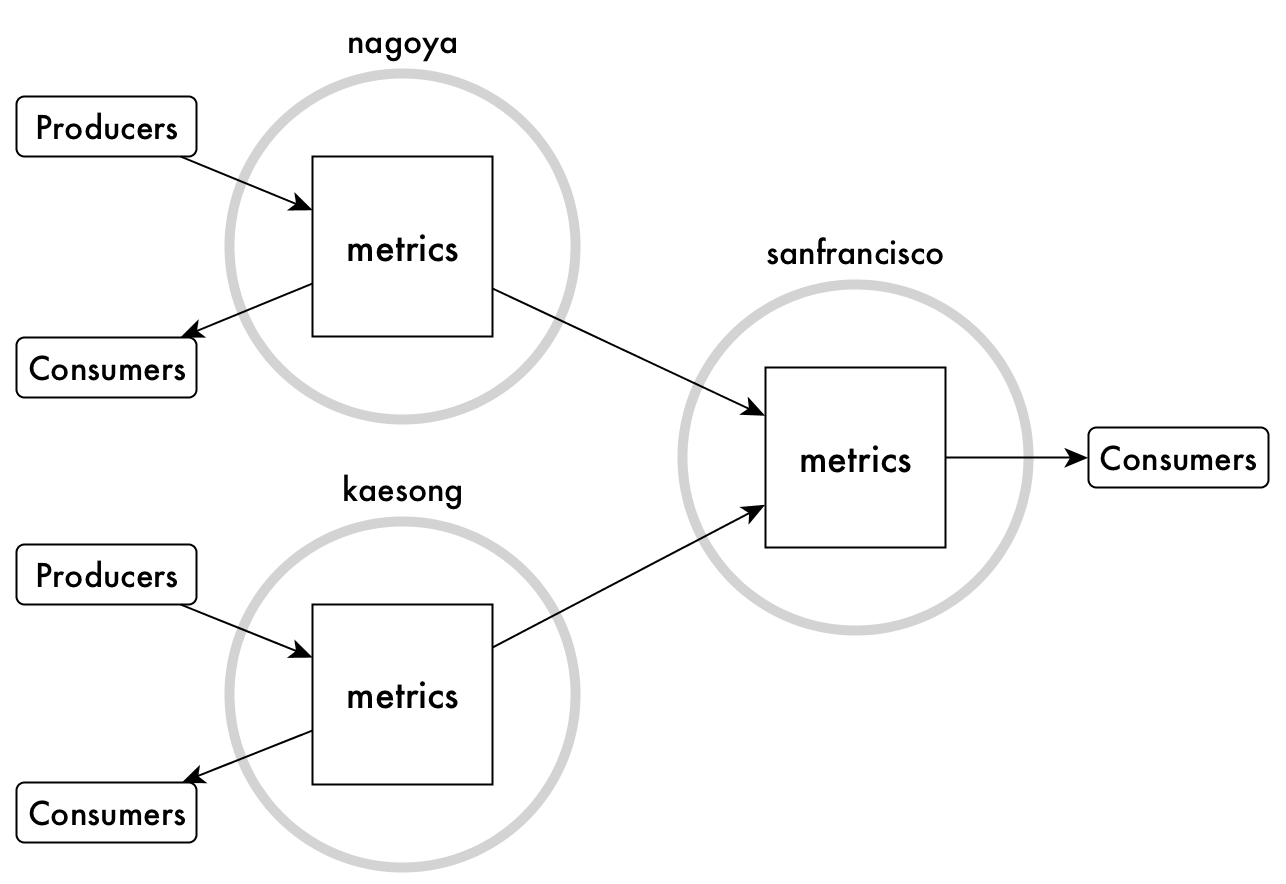
This type of replication, called many-to-one replication, requires that the
topics in each stream have unique names, so that message offsets do not conflict. For
example, suppose both factories have an assembly line named Line 2 and the topic in each
factory's stream for collecting metrics from this line is named line_2. At
some point, the Nagoya factory and the Kaesong factory both replicate messages that use the
same offsets. Since offsets are replicated together with messages, messages can be
overwritten in this case.
To avoid this type of problem, the sensors for Line 2 in
the Nagoya factory might publish to a topic named line_2_nagoya, the
sensors for Line 2 in the Kaesong factory might publish to a topic named
line_2_kaesong, and so on. The consolidated stream in San Francisco would
contain the topics line_2_nagoya and
line_2_kaesong.
Multi-Master Replication
Another kind of
of replication that can be useful is multi-master replication. You can use it
when you need two streams, both to send updates to and receive updates from the other
stream. Each stream is a replica and an upstream source. HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric Streams keeps both
streams synchronized with each other. This type of replication is also simple to set up with
the command maprcli stream replica autosetup.
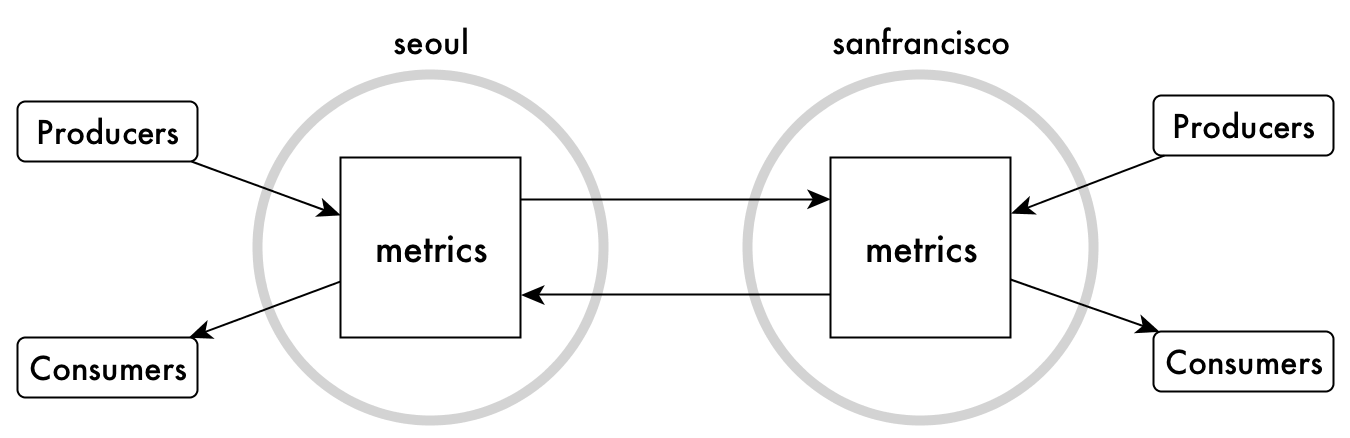
As with many-to-one replication, the names of the topics in each stream must be unique across both streams, so that offsets for messages do not conflict.
Updates are applied to replica streams by Data Fabric gateways. See Gateways and Stream Replication for more information.