Kafka Schema Registry Security
Describes security mechanisms for Kafka Schema Registry.
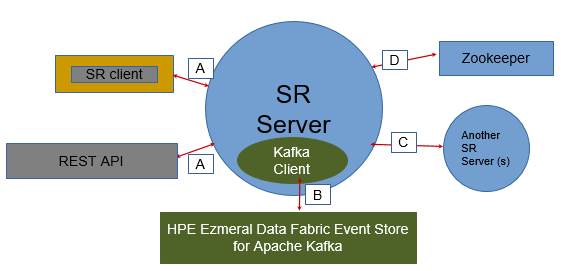
Schema Registry Communication Paths
The following image depicts the Schema Registry communication paths:
The following table lists the supported security mechanisms for the Schema Registry
communication paths:
NOTE
Path B does not have a network connection and therefore does not
need to be secured. However, impersonation works seamlessly for this path through Schema
Registry Server. | Security Features | Supported Mechanisms | Communication Paths Secured |
| Authentication | MapR-SASL (ticket-based security) | D – Schema Registry Server and ZooKeeper |
| A - Schema Registry Client and Schema Registry Server | ||
| C – Schema Registry Server and Schema Registry Server | ||
| Basic (PAM) | A - Schema Registry Client and Schema Registry Server | |
| C – Schema Registry Server and Schema Registry Server | ||
| Cookie | A - Schema Registry Client and Schema Registry Server | |
| C – Schema Registry Server and Schema Registry Server | ||
| Encryption | MapR-SASL (ticket-based security) | D - Schema Registry Server and ZooKeeper |
| A - Schema Registry Client and Schema Registry Server | ||
| C -Schema Registry Server and Schema Registry Server | ||
| SSL/TLS | A - Schema Registry Client and Schema Registry Server | |
| C - Schema Registry Server and Schema Registry Server | ||
| Authorization | Based on filesystem permissions. | A - Schema Registry Client and Schema Registry Server |
| Impersonation | User impersonation | A - Schema Registry Client and Schema Registry Server |
| B – Schema Registry Server to Streams for Apache Kafka | ||
| C - Schema Registry Server and Schema Registry Server | ||
| Auditing | Not supported | -- |