Remote Direct Memory Access
This page introduces Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA), describes the advantages of RDMA over TCP/IP, documents RDMA system requirements, and lists commands you can use to enable RDMA.
What is RDMA?
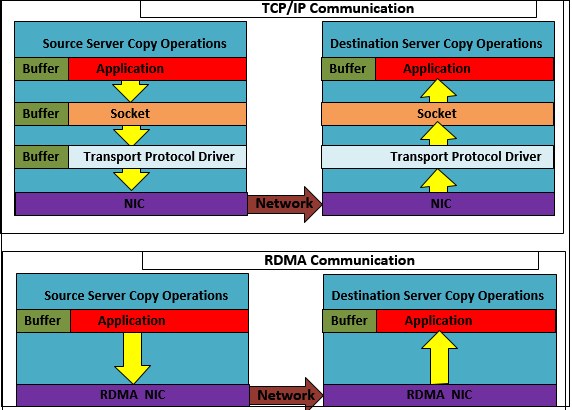
TCP/IP communication uses copy operations that involve user-kernel context switching, user-kernel memory copies, Linux kernel interrupt processing, and kernel packet processing. TCP/IP suffers from two major problems:
- TCP/IP consumes significant CPU cycles and memory resources
- TCP/IP has large end-to-end latency
Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) mitigates these major problems by copying data directly between virtual memory buffers on two different machines, resulting in lower latency, higher throughput, and smaller CPU footprint.
RDMA transfers do not involve the CPU, and there are no context switches. Transfers occur in parallel with other system operations.
The following diagram compares TCP and RDMA operations:
Supported RDMA Type
There are two kinds of RDMA protocols in existence - RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) and iWARP. HPE Data Fabric supports only RoCE.
When HPE Data Fabric Uses RDMA
HPE Data Fabric uses RDMA when it needs to transfer data between:
- Fileclient, FUSE to MFS
- NFS clients and NFS gateway
- MFS instances
RDMA System Requirements
To benefit from RDMA, your system needs to have a Network Interface Card (NIC) that supports RDMA. HPE Data Fabric is tested with Mellanox cards, but any NIC that supports RDMA should work. Ensure that you have Infiniband support installed. To install Infiniband support, run:
yum -y groupinstall "Infiniband Support" ibv_devinfo | grep "PORT_ACTIVE"If the command returns the active ports, then your NIC(s) support(s) RDMA.
# ibv_devinfo | grep "PORT_ACTIVE"
state: PORT_ACTIVE (4)
state: PORT_ACTIVE (4)- Run:
The output returns the Infiniband devices. For example:ibv_devicesdevice node GUID ------ ---------------- mlx4_0 040973ffffd661f0 mlx4_1 b88303ffff9e5440 - Run:
to determine the RDMA NIC. For example:ls /sys/class/infiniband/<Infiniband_Device_Name>/device/net/
Here, the NIC is eno5d1.ls /sys/class/infiniband/mlx4_0/device/net/ eno5d1 ib0 - To confirm that this NIC exists, run:
For example:ip a | grep <NIC>ip a | grep eno5d1 6: eno5d1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000 inet 10.163.160.63/21 brd 10.163.167.255 scope global noprefixroute eno5d1 inet 10.163.160.47/24 scope global eno5d1:~m0
RDMA is automatically enabled only when the NICs/nodes are RDMA capable. HPE Data Fabric automatically uses TCP/IP when the system does not support RDMA.
Enabling RDMA
By default, RDMA is disabled on all nodes. To enable RDMA, use any of the following options:
- For the cluster, set
/opt/mapr/bin/maprcli config save -values '{"support.rdma.transport":"1"}' - For the node, in the
/opt/mapr/conf/env_override.shfile on that node, setexport MAPR_RDMA_SUPPORT=true
- Enable RDMA on the cluster and node.
- In the
/opt/mapr/conf/mfs.conffile on that node, setmfs.listen.on.rdma=1.
- Enable RDMA on the cluster and node.
- Enable RDMA on all MFS nodes in the cluster.
- In the
/opt/mapr/conf/nfsserver.conffile on that NFS node, setNfsRdmaToMfs=1.
- Enable RDMA on the cluster and node.
- Set the property
fs.mapr.disable.rdma.transporttofalsein the/opt/mapr/hadoop/hadoop-<version>/etc/hadoop/core-site.xmlfile.
NFS Port for RDMA Communication
NfsRdmaPort parameter in
/opt/mapr/conf/nfsserver.conf to the desired port. For
example:NfsRdmaPort=200500 causes NFS servers to use TCP to communicate with NFS clients.
NFS Mount With RDMA
mount -o vers=3,proto=rdma,port=20049 <NFSserver IP>:<directory> <mount point>RDMA Specific Commands
mrconfig commands to display RDMA information: - mrconfig rdma dumpServerInfo – Displays RDMA server information.
- mrconfig rdma listEndPoints – Displays RDMA
connection information similar to
netstatfor RPC listings.