KSQL Security
Discusses KSQL security topics.
KSQL Security Overview
By default, KSQL is secure when installed on a secure cluster. A secure cluster is a cluster installed with the default security (MapR-SASL) enabled. Default security provides authentication, encryption, impersonation, and authorization. For encryption, SSL/TLS protocols are supported.
KSQL Communication Paths
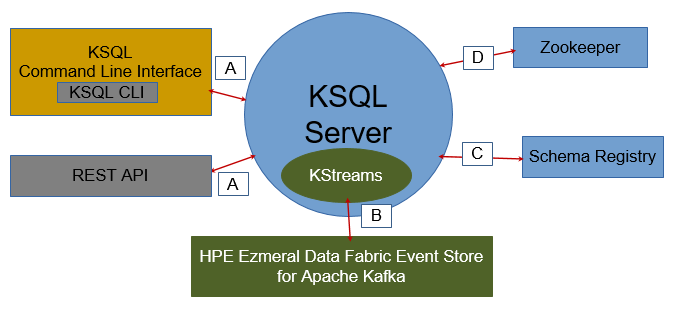
| Security Features | Supported Mechanisms | Communication Paths Secured |
| Authentication | MapR-SASL (ticket-based security) | D - KSQL Server and ZooKeeper |
| A - KSQL client (KSQL CLI/REST API) and KSQL server | ||
| C - KSQL Server and Schema Registry | ||
| Basic (PAM) | A - KSQL client (KSQL CLI/REST API) and KSQL server | |
| C -KSQL Server and Schema Registry | ||
| Cookie | A - KSQL client (KSQL CLI/REST API) and KSQL server | |
| C - KSQL Server and Schema Registry | ||
| Encryption | MapR-SASL (ticket-based security) | D - KSQL Server and ZooKeeper |
| A - KSQL client (KSQL CLI/REST API) and KSQL server | ||
| C -KSQL Server and Schema Registry | ||
| SSL/TLS | A - KSQL client (KSQL CLI/REST API) and KSQL server | |
| C - KSQL Server and Schema Registry | ||
| Authorization | Based on filesystem permissions | A - KSQL client (KSQL CLI/REST API) and KSQL server |
| Impersonation | User impersonation | A - KSQL client (KSQL CLI/REST API) and KSQL Server |
| B - KSQL Server to Streams for Apache Kafka | ||
| C - KSQL Server and Schema Registry | ||
| Auditing | Not supported | -- |
Impersonation
See KSQL Impersonation.
Authorization
See KSQL Authorization.
Authenticating to KSQL
--auth
flag and indicate the authentication type for your KSQL environment, for
example:ksql --auth MAPRSASL http://<ip-address>:8084
//Note that 8084 is the default port for KSQL. --auth is MAPRSAL. The
--auth flag accepts the following values:--auth BASIC(For basic or PAM, the system prompts users for a username and password.)--auth MAPRSASL(For MapR-SASL, a mapr user ticket is used.)--auth NONE(For none, authentication is disabled.)
--cluster option with the remote cluster name, as
shown:ksql --cluster my.mapr.cluster https://<ip-address>:8084KSQL COMMANDS
The KSQL COMMANDS internal topic is used to backup information about KSQL streams, KSQL tables, KSQL persistent queries, and so on. KSQL uses KSQL COMMANDS to restore the KSQL server state in case there is a fault or server restart.
Each KSQL Server cluster has a unique service ID which is provided through the
ksql.service.id property. By default, the
kslq.service.id is _default. To provide additional
security, ksql.service.id-specific folders are created in the
ksql-internal-stream stream.
/apps directory has only write access to mapr
user. Therefore, the /apps/ksql directory cannot be modified or deleted by
any user other than mapr user. KSQL ksql.service.id-specific folders are created in the
/apps/ksql/ directory for every KSQL server cluster (represented by
ksql.service.id).
Default Stream
KSQL Server provides a default stream for topics when they are being processed. When KSQL Server is not impersonated (non-interactive or interactive+no-impersonation), the KSQL Server default stream is used.
KSQL Cleanup
The KSQL cleanup feature is integrated to ensure that the underlying KSQL state (such as internal topics) are cleaned up correctly. See Application Reset Tool for more information.
Deployment
The Warden service (mapr-warden) manages KSQL Servers in clusters.
ksql.service.id) is uniquely created for the KSQL
implementation; this means that the user associated with the service ID
cannot grant permissions to other users to use the same service ID.Cookie Authentication for KSQL
User credentials or challenge strings use cookies to sign requests. After cookies are received on the client side, user credentials or challenge strings are erased from memory. For KSQL, when cookies expire, you have to login again to get the new cookies. Default expiration time for cookies is one week.
Specify a Custom KSQL Truststore Location on a Secure Cluster
/opt/mapr/conf/ssl_truststore on a secure cluster; however, you can
specify a custom SSL truststore file location through properties set from the command line
or in the ksql-server.properties file.- Use the Default Truststore File
- To use the default truststore file while working in the KSQL CLI,
run:
ksql https://node1.cluster.com:8084
- Specify a Custom KSQL Truststore from the Command Line
- Use the
--truststoreflag with the directory location where the SSL truststore file is located and the--truststore-passwordwith the truststore password, as shown in the following example:ksql https://node1.cluster.com:8084 --truststore /opt/mapr/conf/ssl_truststore2 --truststore-password test123