Hashed Indexes
A hashed index is a secondary index that distributes keys across logical partitions to avoid creating hot spots when HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric Database updates the index with new keys from the JSON table.
Hot spots occur when data inserted into an indexed field has monotonically increasing values, or when a burst of write activity occurs. The former occurs with timestamp values. The latter occurs when you have a burst of updates on an indexed field over a small range of values. Hashed indexes enable HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric Database to evenly distribute new writes on an index and avoid hot spots.
Hashed indexes support the same conditional queries as non-hashed indexes, except that hashed indexes do not have a guaranteed sort order. Hashed indexes do not support ORDER BY queries due to the distribution of data across logical partitions. Consequently, sorting is performed by the query layer, which can increase the CPU costs and negatively impact performance.
Guidelines on Creating Hashed Indexes
- Create a hashed index on fields with monotonically increasing values, such as timestamp values.
- Create a hashed index on fields that HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric Database updates in bursts of write activity, for example when HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric Database updates a small range of possible values for the indexed field.
- Do not create hashed indexes for ORDER BY queries.
- Use the
maprcli table index listcommand or the Control System to determine if an index is hashed. See maprcli table index list or Listing Indexes. - After you create an index with hashing enabled, you cannot disable hashing.
Example Comparison of a Non-Hashed Index and Hashed Index
The following images depict a non-hashed (default) index and a hashed index. For the
purpose of this example, assume that an index was created on the
DateCreated field of a JSON table in HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric Database. Yellow highlighted areas
indicate updates to the index.
Non-Hashed (Default) Index
DateCreated field updates from the JSON
table to the index. Notice that the dates are sorted within the index and no partitions
exist. Depending on the size of the index, the index may exist on one or multiple
nodes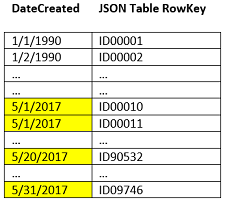
.
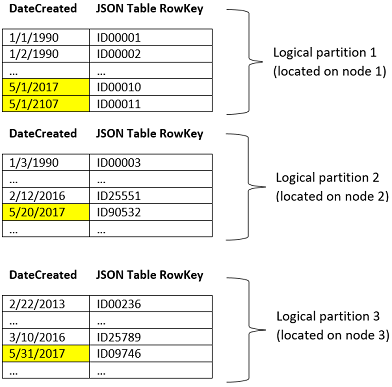
Hashed Index
DateCreated field updates across the index
partitions which reside on different nodes. Notice that dates are sorted within each
partition and each partition resides on a different node.