Restoring the Mirror Relationship
Explains how to restore the mirror relationship between the original read-write volume in the primary datacenter and the promoted read-write volume in the secondary datacenter.
About this task
If the primary datacenter comes back online, the administrator can re-establish the mirror relationship between the original read-write volume in the primary datacenter and the promoted read-write volume in the secondary datacenter.
Note that the two read-write volumes will have different data, since data was written to the promoted mirror while the original source volume was down. The original source volume might also have different data that was written after the last mirror operation, but before the cluster went down. The administrator must decide which data to keep and use as the source.
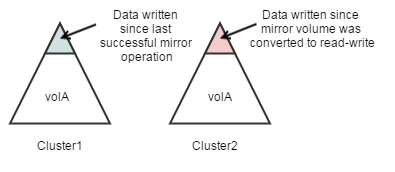
The following sections provide information about how to restore the mirror relationship:
- Preserving volA/Cluster1's Data
Suppose that volA in the primary datacenter contains crucial data that must be preserved, and you want to mirror its data to volA in the secondary datacenter (the same mirror relationship that was established originally). To recreate the original mirror relationship, convert the promoted volume, volA/Cluster2, from a read-write volume to a mirror of volA/Cluster1 by running the following command:
Cluster2> maprcli volume modify -name volA -type mirror -source volA@Cluster1To use the Control System to convert volA/Cluster2 from a read-write volume to a mirror of volA/Cluster1, follow steps for Changing a Standard Volume to a Mirror Volume.
- Preserving volA/Cluster2's Data on volA/Cluster1
Now suppose you want to preserve the data on volA/Cluster2 (in the remote datacenter) but you still want volA/Cluster1 to be the primary volume with volA/Cluster2 as its mirror. From the command line or the Control System, you can save volA/Cluster2's data on volA/Cluster1 and reestablish the original mirror relationship from volA/Cluster1 to volA/Cluster2.
You can use either of the following methods to preserve the data:
From the Control System
About this task
Procedure
-
Stop writing new data to volA/Cluster2 by making this volume read-only:
For detailed steps, see Modifying a Volume.
-
Make volA/Cluster1 a mirror of volA/Cluster2.
For detailed steps, see Changing a Standard Volume to a Mirror Volume.
-
Start mirroring.
For detailed steps, see Starting the Mirror.
-
Promote volA/Cluster1 to a read-write volume.
For detailed steps, see Changing Mirror Volumes to Standard Volumes.
-
Make volA/Cluster2 a mirror of volA/Cluster1.
For detailed steps, see Changing a Standard Volume to a Mirror Volume.
From the Command Line
Procedure
-
Stop writing new data to volA/Cluster2. To be sure no data is written to this volume, make
it read-only by running this command:
Cluster2> maprcli volume modify -name volA -readonly true -
Pull the data from volA/Cluster2 to volA/Cluster1 by making volA/Cluster1 a mirror of
volA/Cluster2.
Cluster1> maprcli volume modify -name volA -type mirror -source volA@Cluster2 -
Start the mirror operation.
Cluster1> maprcli volume mirror start -name volA -
Once mirroring is done, promote volA/Cluster1 to a read-write volume. Note that the mirror
relationship breaks at this point.
Cluster1> maprcli volume modify -name volA -type rw -
Make volA/Cluster2 a mirror of volA/Cluster1.
Cluster2> maprcli volume modify -name volA -type mirror -source volA@Cluster1