Data Tiering
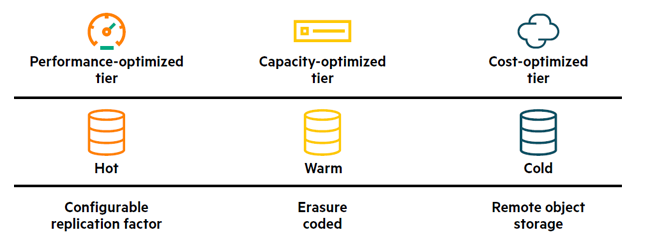
Data tiering is the process by which data is moved among storage tiers as a way for a business to ensure that the appropriate data resides on the appropriate storage technology. Typical data tiering includes hot (replicated), warm (erasure coded), and cold (remote storage) tiers.
Data tiering is the process by which data is moved among storage tiers as a way for a business to ensure that the appropriate data resides on the appropriate storage technology.
A typical use of data tiering for a business is to balance performance, capacity, and cost:
- Data that is active and frequently accessed is referred to as "hot" data and is stored on the highest-performance storage technologies, which have a higher cost.
- Data that is less-frequently accessed can be stored on lower cost, lower performance storage technologies. This second tier of data is referred to as "warm" data.
- Data that is to be kept in long term storage for archiving, and yet still can be brought back to operational status, is referred to as "cold" data.
For more information about data tiering, see Data Tiering in the HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric documentation.
