Configuring Cross-Cluster Trust
The edftool allows you to configure cross-cluster trust
between either:
- One HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric cluster on bare metal and one HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric on Kubernetes cluster.
- Two HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric on Kubernetes clusters.
Trust allows mirroring between the two clusters and also allows tenants in one cluster to
access data or tenants in the other cluster. All clusters listed in the
mapr-clusters.conf file must have unique names in order to
configure trust.
Compatibility
Cross-cluster operations are supported between HPE Ezmeral Runtime Enterprise clusters running the dataplatform operator with
mapr-core-6.2.0 and other clusters running:
-
dataplatformoperator withmapr-core-6.2 -
dataplatformoperator withmapr-core-6.1 - Bare-metal HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric clusters running release 6.1.0 or release 6.2.0
In this context, the term bare-metal means that HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric is deployed on either a Linux platform or a virtual machine.
About the edftool
The edftool simplifies complex security-related HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric tasks, including:
- Setting up trust between two clusters.
- Exporting the public certificates for each service.
- Exporting the private keys for each service.
- Generating certificate-signing requests for each service.
- Importing new certificates.
The edftool tool resides in the admincli-0 pod, but
the tool can also be run remotely from a Linux system with admin-level
kubectl access to the cluster namespace. A client system
running the edftool tool must have Keytool JDK utility, which is
present if Java is installed. The tool uses SSH to log into both clusters and does
the following:
- Generates login and service tickets on both clusters.
- Persists the cluster information for both clusters into the
ssl_trustoreandmapr-clusters.conffiles.Each Data Fabric cluster has a configuration file,
mapr-clusters.conf, that specifies the other Data Fabric clusters that this cluster can connect to. The file identifies the other clusters by specifying the cluster CLDB nodes.For more information about the
mapr-clusters.confconfiguration file, see mapr-clusters.conf in the HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric documentation. - For each instance of HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric on Kubernetes,
edftoolgenerates akubectlpatch. Thekubectlpatch enables secrets to persist the trust information after a pod restarts.
Accessing the edftool help
-
Log into the
admincli-0pod by executing the following command:kubectl exec -it -n <pod-namespace> admincli-0 -- /bin/bash -
Execute the following command:
edftoolThe tool displays the command help:
$ edftool Tool to help with some of the more complex tasks in the Data Fabric Usage: edftool [command] Available Commands: cluster-trust Setup trust between two clusters export-certs Export the public certs of each serviceexport-keys Export the private keys of each service gen-csrs Generate certificate signing requests for each service help Help about any command import-certs Import new certs (newly signed?) Flags: -h, --help help for edftool Use "edftool [command] --help" for more information about a command. -
You can display detailed information about each command by executing the following command:
edftool <command> --help -
For example:
edftool cluster-trust --help
Setting Up Cross-Cluster Trust
This illustration depicts the process of setting up cross-cluster trust:
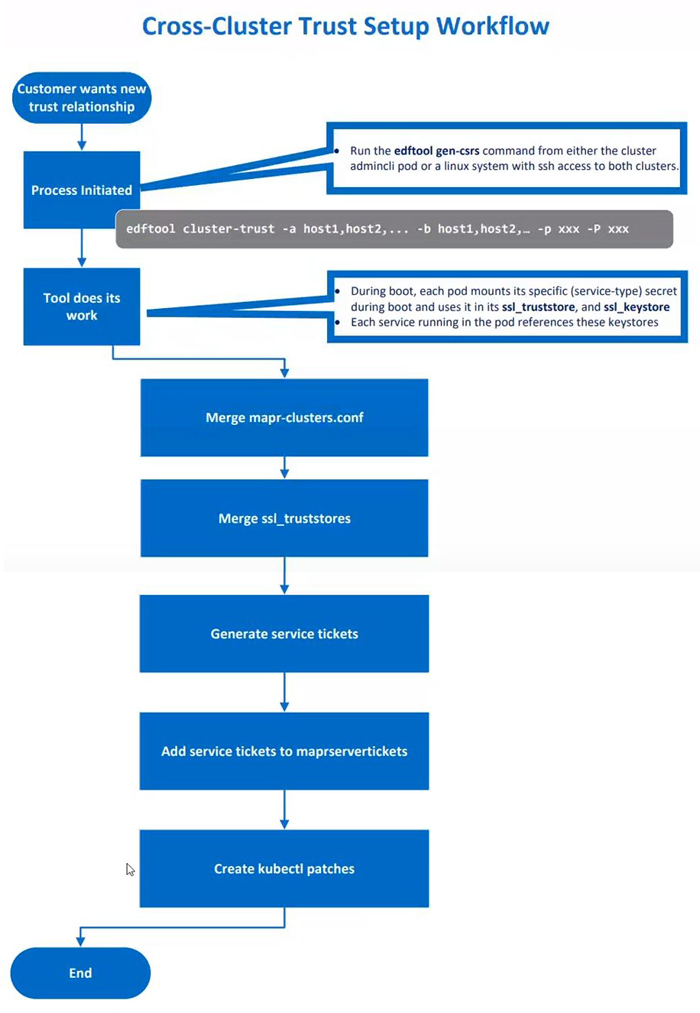
To set up cross-cluster trust, do the following:
-
Execute the following command on either the Kubernetes cluster or the Data Fabric client where the
edftoolis installed:kubectl exec -it -n <pod-namespace> admincli-0 -- /bin/bash -
Change to the
/tmpdirectory to facilitate logging for theedftool:cd /tmp -
Execute the
edftool cluster-trustcommand with the required parameters.The following example sets up cross-cluster trust between an HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric on Kubernetes and a bare-metal HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric cluster:
edftool cluster-trust -a 192.168.11.41,192.168.11.42,192.168.11.43 -p mapr -b 10.123.7.1, 10.123.7.2, 10.123.7.2 -P mapr -S 5000In the example:
- The first three IP addresses are used for the nodes that the CLDB pods are running on in the Kubernetes cluster, followed by the Kubernetes cluster password. The Kubernetes cluster contains the table to be replicated and is thus the “local” cluster.
- The next three IP addresses are the IP addresses for the CLDB nodes in the bare-metal cluster, followed by the bare-metal cluster password. The table will be replicated to the bare-metal cluster, which is the “remote” cluster.
-S 5000is the SSH port override for the local Kubernetes Data Fabric cluster.Port 5000 is the default port for containerized Data Fabric clusters. If both clusters were containerized Data Fabric clusters, then another parameter would be required for the remote cluster:
-s 5000.
-
When prompted by the
edftool, run the script specified by the prompt. The script applies the patch that enables the secrets to persist the trust information after a pod restart. Patch script files are namedk8_patch_cluster_<cluster-name>.sh, where<cluster-name>is the name of the cluster to which the patch should be applied.For example:
Please run the script './k8_patch_cluster_mydfcluster.sh' on a client with kubectl access to it and rights to modify secrets and configmaps in the dataplatform namespace.
If you are establishing trust between a Kubernetes Data Fabric cluster and a bare-metal HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric cluster, then a patch is created for the Kubernetes Data Fabric cluster only.
If you are establishing trust between two Kubernetes Data Fabric clusters, then two patches are created. You must do the following:
- Run one of the scripts in the
adminclipod on the local Kubernetes cluster. - Copy the other script to a node that has client access to the remote Kubernetes cluster.
- Run the script on the remote Kubernetes cluster.
- Run one of the scripts in the
- Check the screen output for errors when the operation completes.
- Log in to the remote
cluster:
maprlogin password -cluster <cluster-name> -
Execute the following command to view files and directories on the remote cluster, thereby ensuring correct trust configuration:
hadoop fs -ls /mapr/<cluster-name>
You should now be able log in to the remote cluster from the local cluster, set up a volume on one cluster and a mirror volume on the other cluster, and start replication. See Creating Remote Mirrors (link opens in a new browser tab/window).
Changes that require reconfiguration
You must reconfigure cross-cluster trust by running the edftool in the following circumstances:
- The IP address of a CLDB pod on the Kubernetes cluster changes.
- Additional CLDB pods are created.
To identify the full set of IP addresses for the CLDB nodes on the Kubernetes
cluster, see the cldbLocations values for the
<cluster-name>-external-cm in the
hpe-externalclusterinfo namespace. The
dataplatform operator automatically generates the
external-cm ConfigMap to indicate the current values for
various cluster parameters.